How to operate a drone? It’s a question many ask, intrigued by the possibilities of aerial photography and exploration. This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough, from pre-flight checks and essential controls to advanced techniques and safety regulations. We’ll demystify the process, equipping you with the knowledge and confidence to take to the skies responsibly.
Mastering drone operation involves understanding not only the technical aspects of flight but also the crucial safety procedures and legal considerations. This guide will cover all these aspects, breaking down complex concepts into easily digestible steps. Whether you are a beginner or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this resource offers practical advice and expert insights to help you navigate the exciting world of drone piloting.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before you even think about taking off, a thorough pre-flight check is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful drone flight. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, damage to your drone, or even injury. This section details the importance of pre-flight checks and provides a comprehensive checklist to follow.
Pre-Flight Checklist Importance
Pre-flight checks are paramount for mitigating risks associated with drone operation. Checking battery levels prevents mid-flight power failures, while inspecting propellers ensures they are free from damage and will function correctly. Verifying GPS signal strength guarantees accurate positioning and helps prevent uncontrolled flight.
Comprehensive Pre-Flight Checklist
A systematic approach is key. Follow these steps before each flight:
- Battery Check: Ensure the drone battery is fully charged and displays a healthy charge level. Consult your drone’s manual for specific voltage recommendations.
- GPS Signal Strength: Verify a strong GPS signal is acquired. Weak signals can lead to inaccurate positioning and loss of control.
- Propeller Inspection: Carefully examine each propeller for any damage, cracks, or imbalances. Replace any damaged propellers immediately.
- Gimbal Check (if applicable): If your drone has a gimbal, ensure it’s properly calibrated and functioning correctly.
- Radio Control Check: Test your controller’s connection to the drone. Ensure all controls respond smoothly.
- Environmental Assessment: Check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation). Avoid flying in strong winds or inclement weather.
- Flight Area Assessment: Choose a safe and open area, free from obstacles and people. Check for airspace restrictions.
Pre-Flight Inspection Procedure, How to operate a drone
A step-by-step approach ensures nothing is missed:
- Power on the drone and controller, ensuring a stable connection.
- Check the battery level on the controller display. If the battery is low, recharge it.
- Observe the GPS indicator lights. Wait until a solid signal is established.
- Visually inspect each propeller for any damage or debris.
- Calibrate the gimbal (if applicable), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration of the drone’s sensors.
- Once all checks are complete and satisfactory, proceed to the next steps.
Drone Model Pre-Flight Requirements Comparison
| Drone Model | Battery Check (Voltage Range) | GPS Check (Signal Strength Indicator) | Propeller Check (Visual Inspection) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | 10.8V – 16.8V | 3-5 bars (typically) | Visual check for cracks or damage |
| Autel Evo II | 11.1V – 15.2V | LED indicator on drone | Visual check for cracks or damage |
| Parrot Anafi | 7.6V – 11.1V | App display | Visual check for cracks or damage |
| Skydio 2 | Variable; check app | App display | Visual check for cracks or damage |
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation: How To Operate A Drone
Mastering drone controls is fundamental to safe and effective operation. This section explains the basic controls, flight modes, and GPS navigation techniques.
Basic Drone Controls
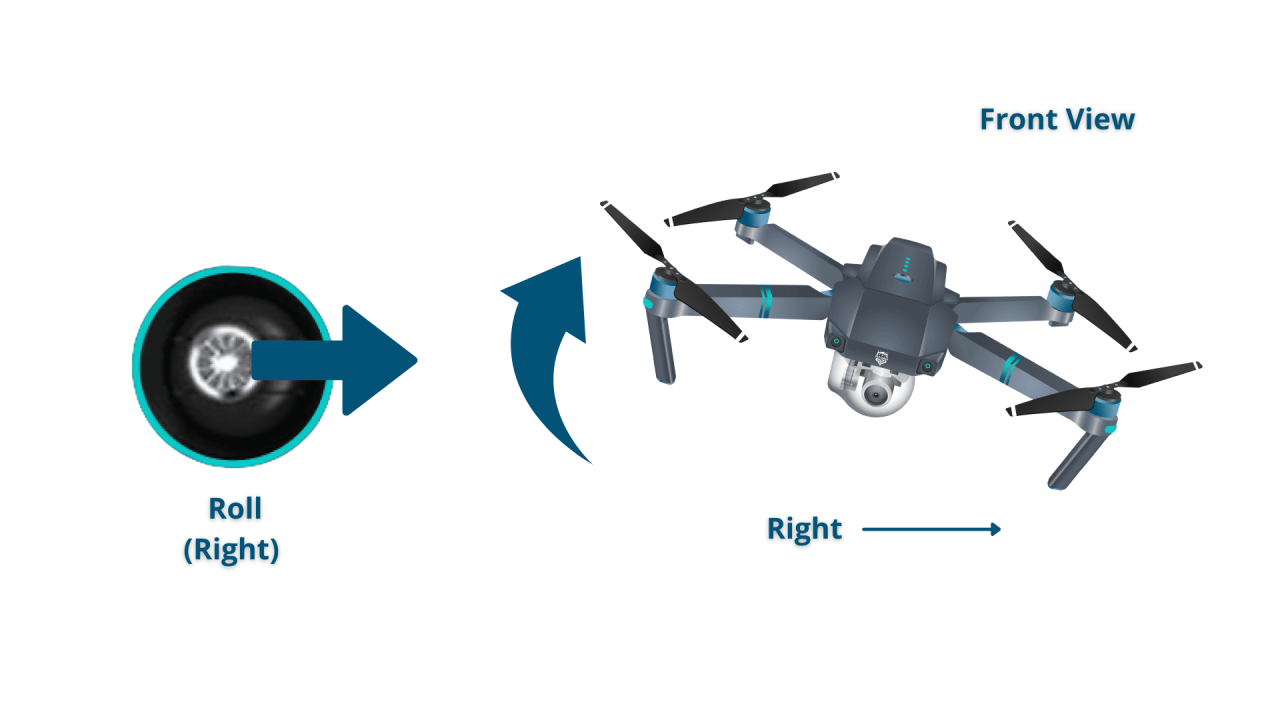
Most drones utilize two joysticks on the controller. The left stick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right stick controls the drone’s direction and speed. Buttons on the controller activate additional functions such as taking photos, recording videos, and returning to home.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various skill levels and flight situations. Beginner modes typically limit speed and responsiveness, while Sport or Manual modes offer greater control and speed but require more experience.
- Beginner Mode: Limits speed and responsiveness for easier control.
- Sport Mode: Increases speed and responsiveness, requiring more skill.
- Manual Mode: Offers full control over all aspects of flight, demanding expertise.
- Altitude Hold: Maintains a consistent altitude, simplifying flight.
- GPS Assisted Flight: Uses GPS signals for precise positioning and stability.
Smooth and Controlled Drone Maneuvers
Smooth maneuvers are achieved through gradual stick movements. Avoid sudden inputs, especially in windy conditions. Practice in a safe, open area to develop your skills.
GPS Navigation and Return-to-Home
GPS is essential for precise navigation and safe return. Most drones have a “Return to Home” (RTH) function that automatically guides the drone back to its takeoff point. Ensure a strong GPS signal before activating RTH.
Drone Controller Indicator Lights
The indicator lights on the controller provide critical information about the drone’s status. Understanding their meanings is crucial for safe operation. A visual guide below illustrates this.
(Imagine a visual guide here showing different lights on the controller and their corresponding meanings: e.g., Solid green light = GPS signal acquired, Blinking red light = low battery, etc.)
Taking Off, Landing, and Basic Flight Maneuvers
This section provides a step-by-step guide for safe takeoff, landing, and basic flight maneuvers. Proper techniques are crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring a smooth flight experience.
Safe Drone Takeoff Procedure
A safe takeoff ensures a smooth start to your flight:
- Ensure a strong GPS signal is established.
- Check the battery level again.
- Carefully lift the drone slightly off the ground using the control sticks.
- Slowly increase altitude to a safe height.
- Once at a safe height, proceed with the intended flight maneuvers.
Safe and Controlled Landing Procedure
A smooth landing is equally important:
- Gradually lower the drone’s altitude.
- Reduce speed as you approach the ground.
- Gently set the drone down on a flat, stable surface.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Maintaining Stable Flight in Windy Conditions
Flying in windy conditions requires extra caution. Adjust your flight style to compensate for wind gusts. Maintain a consistent altitude and avoid sudden movements. If the wind becomes too strong, land the drone immediately.
Basic Flight Maneuvers
These maneuvers form the foundation of drone piloting:
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone left or right.
- Forward/Backward/Sideways Movement: Moving the drone in any direction.
Emergency Landing Procedures
In case of an emergency, follow these steps:
- Immediately attempt to regain control of the drone.
- If control is lost, activate the Return to Home (RTH) function (if available).
- If RTH fails, attempt a controlled descent, lowering the drone gently to the ground.
- If a controlled descent is not possible, prioritize landing in a safe area, minimizing potential damage.
Photography and Videography with Drones
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning photos and videos. This section explains how to optimize camera settings and compose compelling aerial shots.
Adjusting Camera Settings
Optimal image and video quality requires proper camera settings. Adjust settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to match lighting conditions. Experiment to find the best settings for your drone and camera.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Effective composition is key. Use the rule of thirds, leading lines, and other photographic principles to create visually appealing images. Experiment with different angles and perspectives.
Camera Angles and Their Effects
Different camera angles dramatically impact the final product. High-angle shots offer a wide overview, while low-angle shots emphasize size and scale. Side angles provide a unique perspective.
Flight Patterns for Various Perspectives
Strategic flight patterns enhance storytelling. Circular patterns can create dynamic shots, while tracking shots follow a moving subject. Experiment with different patterns to find what works best for your subject.
Common Photography and Videography Mistakes to Avoid

- Overexposed or underexposed images.
- Shaky footage due to wind or improper piloting.
- Boring compositions lacking visual interest.
- Ignoring the rule of thirds.
- Not utilizing various camera angles.
- Ignoring the lighting conditions.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone. This section Artikels a maintenance schedule and common troubleshooting tips.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule helps prevent issues and ensures your drone remains in optimal condition:
- Cleaning: Regularly clean the drone body, propellers, and camera lens using a soft cloth.
- Battery Care: Store batteries in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight. Avoid fully discharging or overcharging batteries.
- Gimbal Care (if applicable): Gently clean the gimbal and avoid jarring movements that could damage it.
- Firmware Updates: Regularly check for and install firmware updates to improve performance and stability.
- Visual Inspection: Before each flight, conduct a thorough visual inspection of the drone’s components.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Understanding common problems and their solutions is crucial for efficient troubleshooting:
| Issue | Cause | Solution | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, damaged power switch | Charge battery, replace battery, inspect power switch | High |
| Weak GPS signal | Poor satellite reception, interference | Move to a location with better GPS reception | Medium |
| Gimbal malfunction | Mechanical failure, software glitch | Recalibrate gimbal, check for physical damage, contact support | Medium |
| Propeller damage | Collision, impact | Replace damaged propellers | Medium |
| Camera issues | Software error, dirty lens | Restart drone, clean lens | Low |
Handling Minor Repairs and Seeking Professional Help
Minor repairs like replacing propellers are straightforward. However, more complex repairs should be handled by qualified technicians. Attempting complex repairs yourself can void warranties and cause further damage.
Proper Drone Storage
Proper storage prolongs the drone’s lifespan. Store it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Keep it in a protective case to prevent damage.
Legal and Safety Regulations
Adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for responsible and legal operation. This section discusses the importance of understanding and complying with these regulations.
Importance of Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Drone regulations vary by location. Failing to comply can result in fines, legal action, and potential harm to others. Research and understand the regulations in your area before flying.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the intricacies of flight, including takeoff, navigation, and landing, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone to ensure safe and effective operation. This resource will help you confidently handle your drone in various scenarios.
Restricted and Prohibited Areas for Drone Operation
Many areas restrict or prohibit drone operation. These include airports, military bases, prisons, and areas with sensitive infrastructure. Always check for airspace restrictions using apps or websites.
Rules Regarding Airspace and Flight Restrictions
Airspace restrictions are designated areas where drone operation is limited or prohibited. These restrictions are often implemented to protect aircraft safety and national security. Familiarize yourself with these restrictions before each flight.
Safe and Responsible Flying Around People and Property
Maintain a safe distance from people and property during flight. Avoid flying over crowds or private property without permission. Respect the privacy of others.
Essential Safety Guidelines for Responsible Drone Operation
- Always check weather conditions before flying.
- Never fly beyond your visual line of sight.
- Always maintain awareness of your surroundings.
- Respect airspace restrictions.
- Fly responsibly and avoid endangering others.
- Never fly under the influence of alcohol or drugs.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers, software utilization, and specialized accessories to enhance your drone experience.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers like waypoint navigation and automated flight require more skill and understanding. Waypoint navigation allows you to pre-program a flight path, while automated flight features handle many aspects of the flight autonomously.
Utilizing Drone Software
Drone software offers advanced features and settings. Learn how to utilize these features to optimize your drone’s performance and capture stunning footage.
Capturing Cinematic Shots and Smooth Transitions
Cinematic shots require careful planning and execution. Practice smooth transitions between shots and use creative camera angles to create engaging visuals.
Specialized Drone Accessories
Specialized accessories like ND filters, gimbals, and prop guards enhance performance and capabilities. Research and choose accessories that suit your needs.
Planning and Executing Complex Drone Flight Paths

Complex flight paths require careful planning and precise execution. Use flight planning software to design your path and ensure it is safe and feasible.
Operating a drone is a rewarding experience, offering unique perspectives and creative opportunities. By following the safety guidelines, understanding the controls, and continuously learning and practicing, you can unlock the full potential of your drone. Remember, responsible operation ensures both your safety and the enjoyment of this exciting technology for years to come. Embrace the skies, but always do so with care and consideration.
FAQ Guide
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with automated features are ideal for beginners. Look for models with GPS, obstacle avoidance, and return-to-home functions.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires knowledge of regulations and safe operating procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone and ensure you’re prepared for a safe and productive flight.
Proper training is essential before attempting to operate a drone independently.
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model and usage. Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes of flight time on a single charge.
What happens if I lose the drone’s signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function that automatically brings the drone back to its starting point if the signal is lost. However, always fly within visual line of sight.
Do I need a license to fly a drone?
Regulations vary by country and region. Check with your local aviation authority to determine any licensing or registration requirements before flying.
